Analyze Power for a Stratified Additive RMST Model (Analytic)
Source:R/additive_stratified_analytical.R
additive.power.analytical.RdPerforms power analysis for a stratified, additive RMST model using the analytic variance estimator based on the method of Zhang & Schaubel (2024).
Usage
additive.power.analytical(
pilot_data,
time_var,
status_var,
arm_var,
strata_var,
sample_sizes,
linear_terms = NULL,
L,
alpha = 0.05
)Arguments
- pilot_data
A
data.framecontaining pilot study data.- time_var
A character string for the time-to-event variable.
- status_var
A character string for the event status variable (1=event, 0=censored).
- arm_var
A character string for the treatment arm variable (1=treatment, 0=control).
- strata_var
A character string for the stratification variable.
- sample_sizes
A numeric vector of sample sizes per stratum to calculate power for.
- linear_terms
An optional character vector of other covariate names.
- L
The numeric value for the RMST truncation time.
- alpha
The significance level (Type I error rate).
Value
A list containing:
- results_data
A
data.framewith specified sample sizes and corresponding powers.- results_plot
A
ggplotobject visualizing the power curve.
Details
This function implements the power calculation for the semiparametric additive
model for RMST, given by \(\mu_{ij} = \mu_{0j} + \beta'Z_i\), where i is the
subject and j is the stratum.
The method uses Inverse Probability of Censoring Weighting (IPCW), where weights are derived from a stratified Cox model on the censoring times. The regression coefficient \(\hat{\beta}\) is estimated using a closed-form solution that involves centering the covariates and RMST values within each stratum.
Power is determined analytically from the asymptotic sandwich variance of \(\hat{\beta}\). This implementation uses a robust variance estimator of the form \(A_n^{-1} B_n (A_n^{-1})'\), where \(A_n\) and \(B_n\) are empirical estimates of the variance components.
Examples
set.seed(123)
pilot_df_strat <- data.frame(
time = rexp(150, 0.1),
status = rbinom(150, 1, 0.8),
arm = rep(0:1, each = 75),
region = factor(rep(c("A", "B", "C"), each = 50)),
age = rnorm(150, 60, 10)
)
# Introduce an additive treatment effect
pilot_df_strat$time[pilot_df_strat$arm == 1] <-
pilot_df_strat$time[pilot_df_strat$arm == 1] + 1.5
power_results <- additive.power.analytical(
pilot_data = pilot_df_strat,
time_var = "time", status_var = "status", arm_var = "arm", strata_var = "region",
sample_sizes = c(100, 150, 200),
linear_terms = "age",
L = 12
)
#> --- Estimating parameters from pilot data... ---
#> --- Estimating additive effect via stratum-centering... ---
#> --- Calculating asymptotic variance... ---
#> --- Calculating power for specified sample sizes... ---
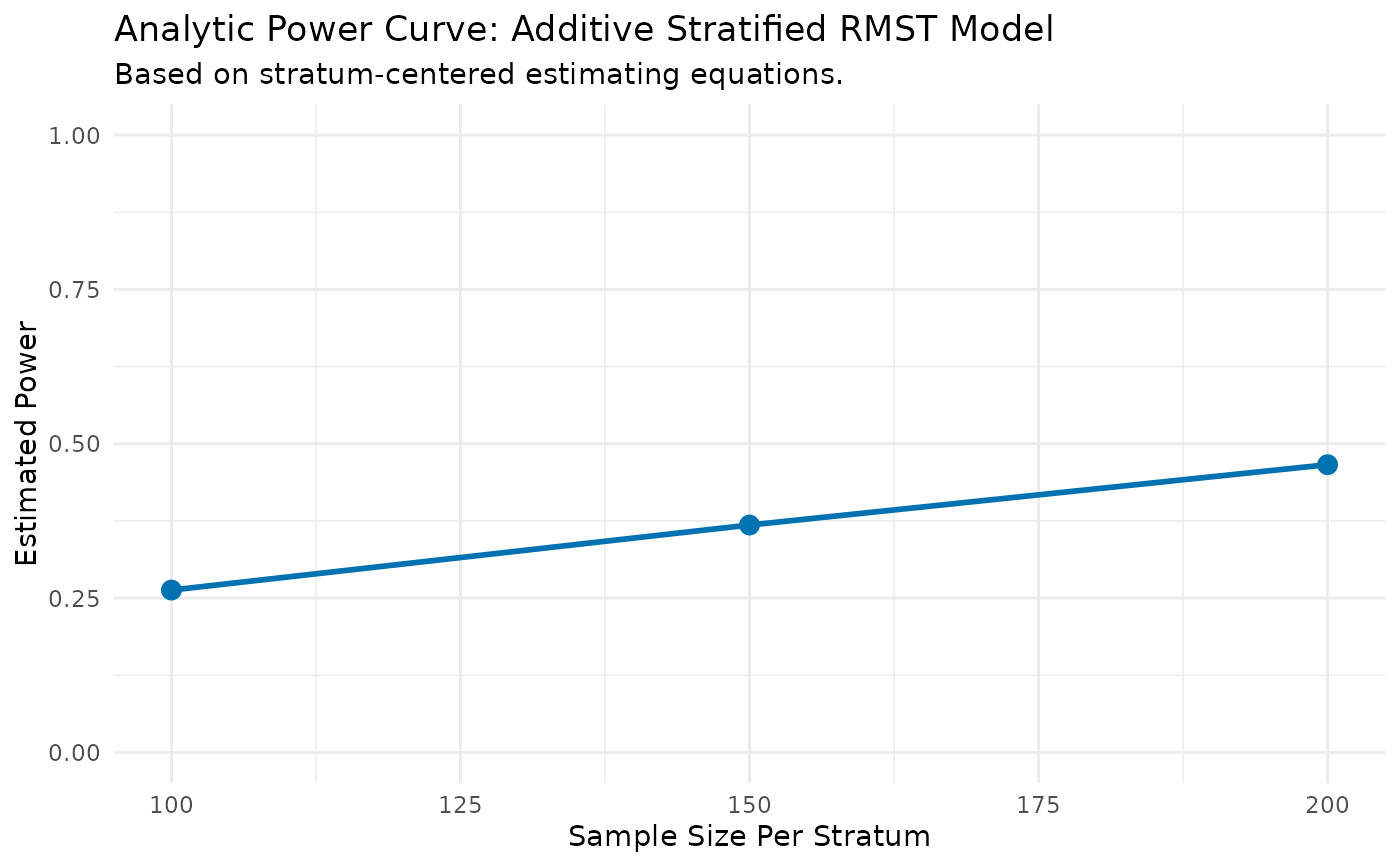
print(power_results$results_data)
#> N_per_Stratum Power
#> 1 100 0.2629389
#> 2 150 0.3682932
#> 3 200 0.4660482
print(power_results$results_plot)